
The absence of a vaccine for preventive purposes makes us rely on antibiotics as the only means of managing gonorrhea. The disease has notoriously developed resistance to outsmart the class of antibiotics used to treat it (Photo: Shutterstock) Infected mothers can also pass it to their babies during childbirth. That means, one can be re-infected even after they had previously had successful treatment against gonorrhea. In addition, infection does not guarantee immunity. For a man, no ejaculation is needed for you to transmit or acquire it. Either through the penis, vagina, mouth or anus, an infected partner can pass it along.
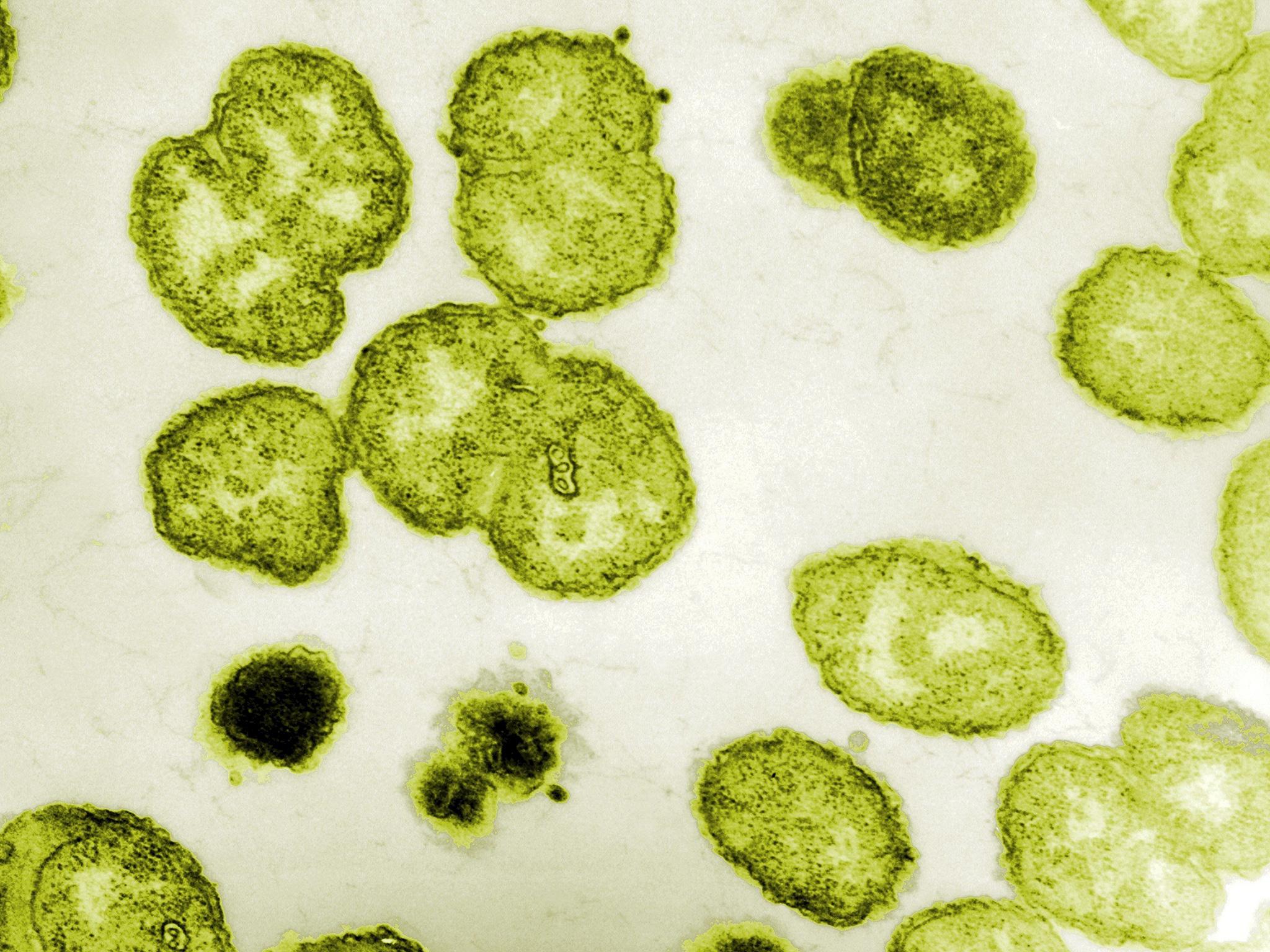

Sexual contact is the main mode of transmission of gonorrhea. It can also cause infection in the eyes, mouth, throat and rectum. The bug infects the cervix, uterus and oviducts (Fallopian tubes) in women and urethra in both men and women.

This alarming recombination continues to stress the already dwindling treatment options and the WHO is concerned about a near future with a superbug that causes untreatable gonorrhea. gonorrhea and other commensal strains of the same genus. The new resistant strains are reported to be as a result of inter-species recombination of genes between the main causative bacterial agent, N. Those of us in public health and healthcare sector understand quite clearly that gonorrhea is quite a stubborn disease.Ĭaused by a bacterium known as Neisseria gonorrhea, the disease has notoriously developed resistance to outsmart the class of antibiotics used to treat it. The World Health Organization (WHO) approximates that 11.4 million gonorrhea cases occur annually in the African region and warns of the emerging threat of “untreatable” gonorrhea.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
